Indonesia is an archipelagic country consisting of various cultures and lives. Various types of culture are the work of our ancestors which have been passed down to our children and grandchildren. Dance, painting and sound arts.
From the art of painting, various types of painting models and painting style motifs emerged. And from the art of painting several types of Indonesian batik models emerged.
Indonesian batik motifs are heavily influenced by the culture of each ethnic group in Indonesia. For example, Papuan batik motifs feature more musical instruments, animals, and humans. Kalimantan batik features more natural motifs such as wood, leaves, or trees. Javanese batik, especially Solo and Yogyakarta, are more influenced by motifs of the elements of the universe, including land, sea, and air. In addition, there are still several batik motifs from various other ethnic groups, such as Bali, Nusa Tenggara, Sulawesi, and Sumatra.
Here are some examples of Indonesian batik motifs based on each tribe:
1. PAPUAN BATIK
source:https://www.orami.co.id/magazine/kain-khas-papua
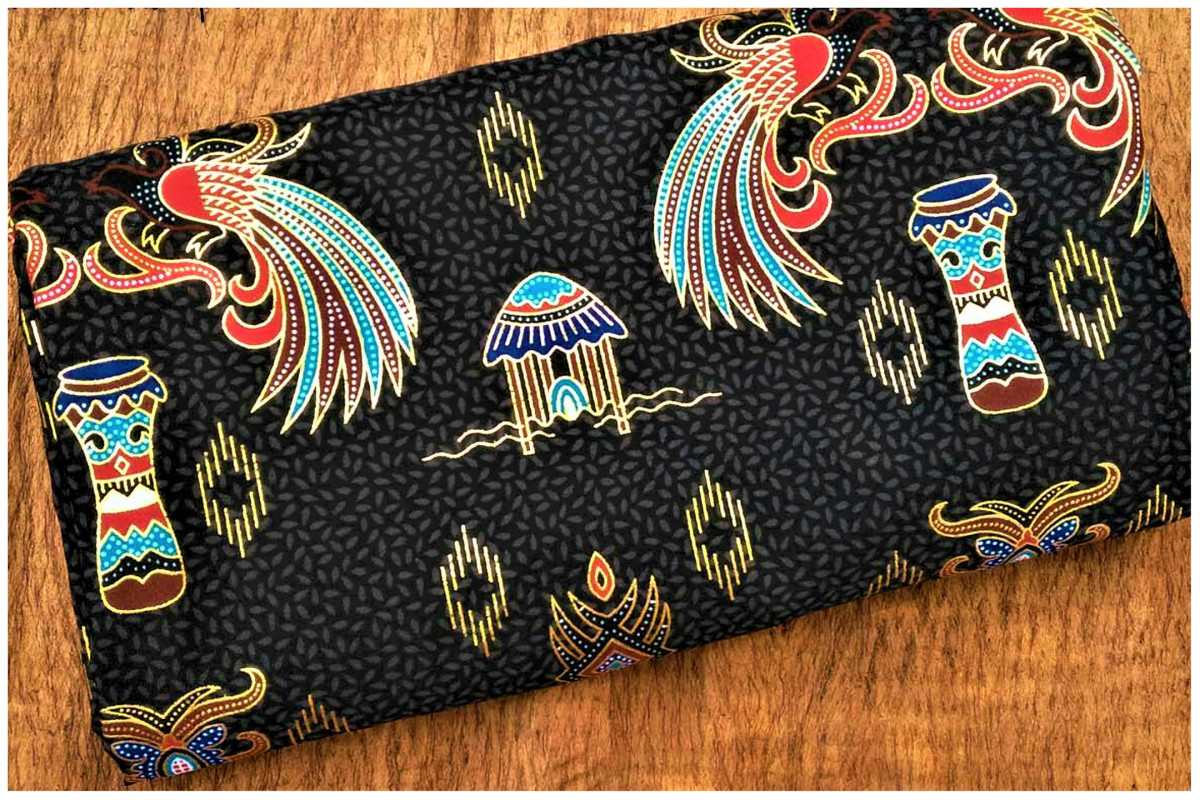

Papuan batik has existed since prehistoric times. Although it is said to be a batik motif, Papuan batik is actually a traditional woven motif from the tribes in Papua. Usually the woven cloth is used for traditional ceremonies.
During the Dutch colonial period, geometric patterns began to appear with a combination of bright colors. And these patterns are still used today in making Papuan batik motifs. Not only geometric motifs are used to make Papuan batik motifs, but also still maintain old motifs such as pictures of birds of paradise, plants and traditional musical instruments.
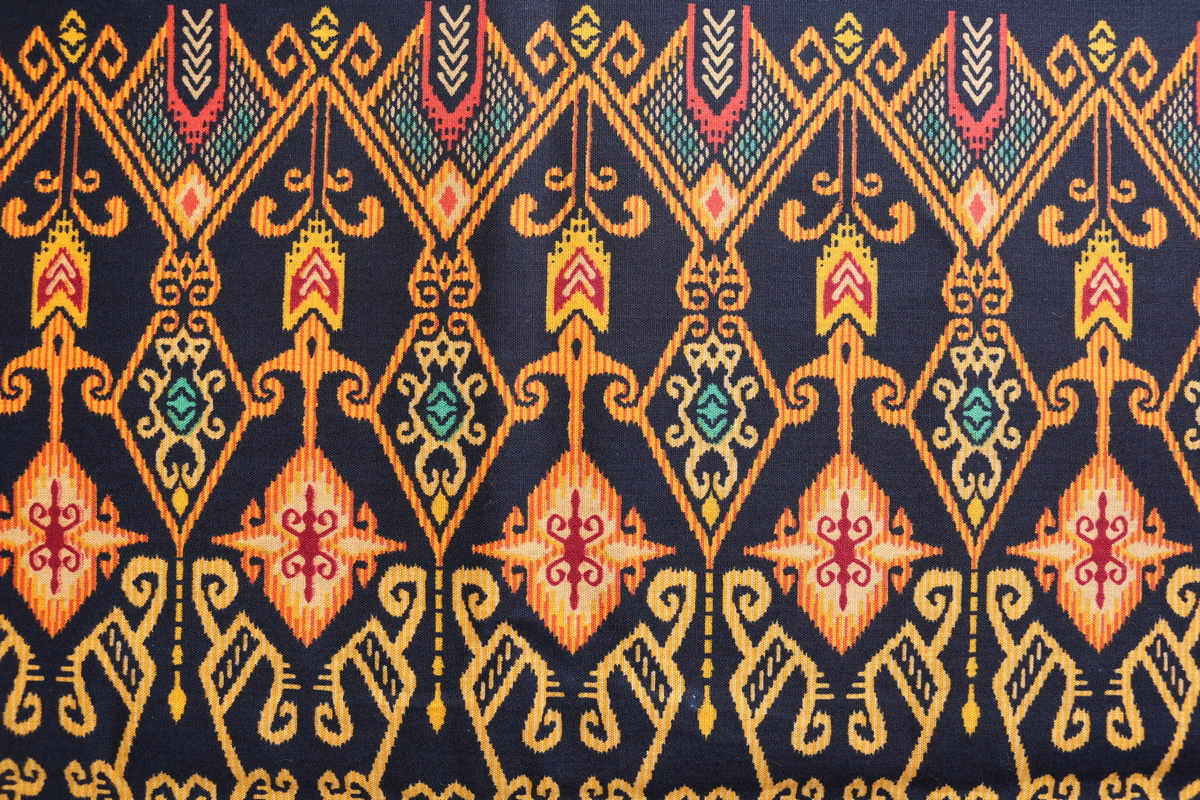
2. KALIMANTAN BATIK

https://www.batikprabuseno.com/artikel/edukasi/batik-kalimantan-timur/

https://pngtree.com/free-png-vectors/batik-kalimantan
Kalimantan batik patterns are greatly influenced by the culture of the tribes that live on the island of Kalimantan. Batik patterns in Kalimantan often use abstract and geometric motifs and contain meaning and values of life. Examples of various Kalimantan batik patterns are: Kembang Munduk motif, Kembang Mengalir motif and various types of Dayak motifs. And usually Kalimantan batik motifs are produced using the RINTANG LILIN (WAX RESIST) technique.
However, many people still mistakenly mention Sasirangan and Tritik Jumputan motifs as Kalimantan batik motifs. Because the manufacturing techniques and the resulting motif footprints are clearly different.
The following are the types of Kalimantan batik motifs: Batang Garing, Spinach Raja, Hornbill, Jaruju Leaves, Dayak Background Gringsing (an example of the assimilation of Javanese and Kalimantan culture), and many more. Each tribe has its own characteristics.
3. JAVANESE BATIK

https://jatenglive.com/tampil-berita/Cantiknya-Ragam-Batik-Khas-Jawa-Tengah
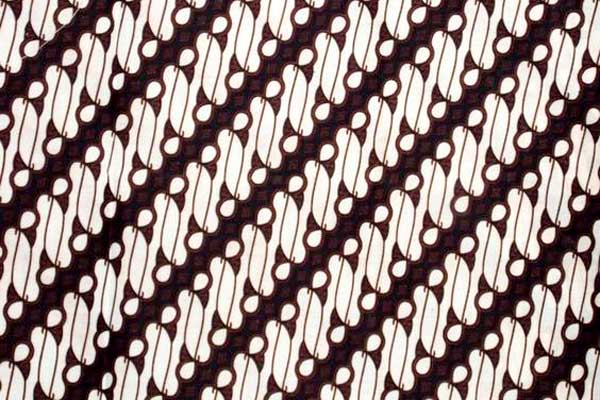
https://lendah.kulonprogokab.go.id/detil/177/10-motif-batik-paling-populer-di-indonesia
Batik patterns on the island of Java are heavily influenced by royal and coastal cultures. An example is Batik Kawung. The history of batik kawung itself comes from the era of the Ancient Mataram kingdom in Central Java. The kawung motif is often used by kings and royal families as a symbol of power and majesty. Batik kawung is also considered a symbol of good luck and fertility. The Kawung batik motif is inspired by the Kawung fruit or better known as Kolang Kaling. With a round oval motif split in two and there is always a dot in the middle as a symbol of the Kawung fruit seeds.
Parang Lerek batik has a long historical root, starting from the era of the Islamic Mataram kingdom in Central Java in the 16th century. This motif was used by the royal family as a symbol of power and nobility. Parang Lerek batik then developed and became popular among the Javanese people as a symbol of elegance and beauty. Parang Lerek batik was inspired by the shape of the waves of the South Sea coast. Because of the many stories about the stories of Javanese kings, especially Solo and Yogyakarta, which are related to the Queen of the South Coast or known as Nyai Roro Kidul. That is why Parang Lerek batik may not be worn by the general public when in the Kasunan Surakarta, Mangkunegaran, Yogyakarta Sultanate and Pakualaman areas. Because the motif may only be worn by the king.
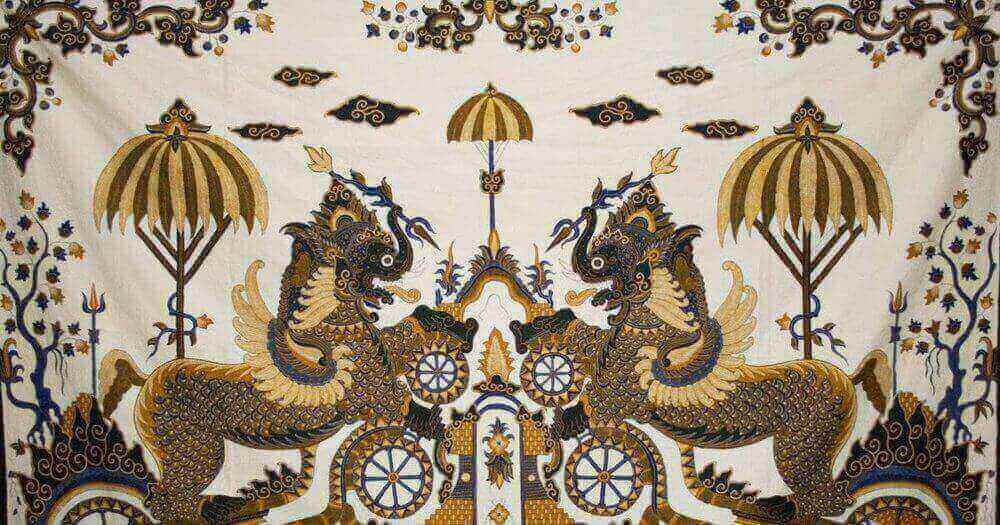
4.BALINESE BATIK
 https://perempuanplatinum.id/sejarah-batik-bali-dan-makna-di-balik-motifnya/
https://perempuanplatinum.id/sejarah-batik-bali-dan-makna-di-balik-motifnya/

https://www.shutterstock.com/search/batik-bali-pattern
The history of Balinese batik began around the 1970s. Pande Kethut Krisna, an artist from Banjar Tegeha, BatuBulan village, Sukowati district, Gianyar regency, Bali. He pioneered the batik industry in Bali. By using a simple batik stamp technique to create Balinese batik. Even at that time the cloth weaving tool was still very simple and was a loom, not a machine.
In general, Balinese batik has the following characteristics:
1. Local motifs include frangipani flowers, birds, natural scenery, fish and the daily life of the Balinese people.
2. Motifs of religious ceremonies or certain rituals that have become customs and culture.
3. Symbols of mythological creatures whose existence is believed by the Balinese people
Those were some examples of batik in the archipelago. The various patterns and motifs of batik are greatly influenced by the customs of the local community. We are truly proud of our ancestral heritage. Let us not forget it, let alone be recognized by other nations.
Let's preserve Indonesian batik. The legacy of the masterpiece of our ancestors that we must protect and preserve. Make batik one of the icons of this country. Be proud to wear Indonesian batik.
If not us, who else?
If not now, when?
Surakarta, June 26, 2024